|
libStatGen Software
1
|
|
libStatGen Software
1
|
Create/Access/Modify/Load Genome Sequences stored as binary mapped files. More...
#include <GenomeSequence.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| GenomeSequence () | |
| Simple constructor - no implicit file open. | |
| void | constructorClear () |
| GenomeSequence (std::string &referenceFilename) | |
| attempt to open an existing sequence | |
| GenomeSequence (const char *referenceFilename) | |
| Smarter constructor - attempt to open an existing sequence. | |
| ~GenomeSequence () | |
| Close the file if open and destroy the object. | |
| bool | open (bool isColorSpace=false, int flags=O_RDONLY) |
| open the reference specified using GenomeSequence::setReferenceName | |
| bool | open (const char *filename, int flags=O_RDONLY) |
| open the given file as the genome (no filename munging occurs). | |
| bool | create (bool isColor=false) |
| void | setProgressStream (std::ostream &progressStream) |
| if set, then show progress when creating and pre-fetching | |
| void | setColorSpace (bool colorSpace) |
| void | setSearchCommonFileSuffix (bool searchCommonFileSuffix) |
| void | setCreateOverwrite (bool createOverwrite) |
| bool | loadFastaData (const char *filename) |
| bool | setReferenceName (std::string referenceFilename) |
| set the reference name that will be used in open() | |
| void | setApplication (std::string application) |
| set the application name in the binary file header | |
| const std::string & | getFastaName () const |
| const std::string & | getReferenceName () const |
| bool | isColorSpace () const |
| tell us if we are a color space reference or not | |
| genomeIndex_t | getNumberBases () const |
| return the number of bases represented in this reference | |
| int | getChromosome (genomeIndex_t position) const |
| given a whole genome index, get the chromosome it is located in | |
| int | getChromosome (const char *chromosomeName) const |
| given a chromosome name, return the chromosome index | |
| int | getChromosomeCount () const |
| Return the number of chromosomes in the genome. | |
| genomeIndex_t | getChromosomeStart (int chromosomeIndex) const |
| given a chromosome, return the genome base it starts in | |
| genomeIndex_t | getChromosomeSize (int chromosomeIndex) const |
| given a chromosome, return its size in bases | |
| genomeIndex_t | getGenomePosition (const char *chromosomeName, unsigned int chromosomeIndex) const |
| given a chromosome name and position, return the genome position | |
| genomeIndex_t | getGenomePosition (int chromosome, unsigned int chromosomeIndex) const |
| given a chromosome index and position, return the genome position | |
| genomeIndex_t | getGenomePosition (const char *chromosomeName) const |
| given the chromosome name, get the corresponding 0 based genome index for the start of that chromosome | |
| genomeIndex_t | getGenomePosition (int chromosomeIndex) const |
| const std::string & | getBaseFilename () const |
| const char * | getChromosomeName (int chromosomeIndex) const |
| void | setDebugFlag (bool d) |
| genomeIndex_t | sequenceLength () const |
| const char * | chromosomeName (int chr) const |
| void | sanityCheck (MemoryMap &fasta) const |
| std::string | IntegerToSeq (unsigned int n, unsigned int wordsize) const |
| bool | wordMatch (unsigned int index, std::string &word) const |
| bool | printNearbyWords (unsigned int index, unsigned int variance, std::string &word) const |
| char | BasePair (char c) const |
| void | dumpSequenceSAMDictionary (std::ostream &) const |
| void | dumpHeaderTSV (std::ostream &) const |
| char | operator[] (genomeIndex_t index) const |
| Return the bases in base space or color space for within range index, ot. | |
| char | getBase (const char *chromosomeName, unsigned int chromosomeIndex) const |
| given a chromosome name and 1-based position, return the reference base. | |
| uint8_t | getInteger (genomeIndex_t index) const |
| void | set (genomeIndex_t index, char value) |
| uint8_t * | getDataPtr (genomeIndex_t index) |
| obtain the pointer to the raw data for other access methods | |
| void | getReverseRead (std::string &read) |
| void | getReverseRead (String &read) |
| int | debugPrintReadValidation (std::string &read, std::string &quality, char direction, genomeIndex_t readLocation, int sumQuality, int mismatchCount, bool recurse=true) |
| void | getString (std::string &str, int chromosome, uint32_t index, int baseCount) const |
| void | getString (String &str, int chromosome, uint32_t index, int baseCount) const |
| void | getString (std::string &str, genomeIndex_t index, int baseCount) const |
| void | getString (String &str, genomeIndex_t index, int baseCount) const |
| void | getHighLightedString (std::string &str, genomeIndex_t index, int baseCount, genomeIndex_t highLightStart, genomeIndex_t highLightEnd) const |
| void | print30 (genomeIndex_t) const |
| genomeIndex_t | simpleLocalAligner (std::string &read, std::string &quality, genomeIndex_t index, int windowSize) const |
| int | getMismatchCount (std::string &read, genomeIndex_t location, char exclude='\0') const |
| Return the mismatch count, disregarding CIGAR strings. | |
| int | getSumQ (std::string &read, std::string &qualities, genomeIndex_t location) const |
| brute force sumQ - no sanity checking | |
| void | getMismatchHatString (std::string &result, const std::string &read, genomeIndex_t location) const |
| void | getMismatchString (std::string &result, const std::string &read, genomeIndex_t location) const |
| void | getChromosomeAndIndex (std::string &, genomeIndex_t) const |
| void | getChromosomeAndIndex (String &, genomeIndex_t) const |
| bool | checkRead (std::string &read, std::string &qualities, std::string &cigar, int &sumQ, int &gapOpenCount, int &gapExtendCount, int &gapDeleteCount, std::string &result) const |
| check a SAM format read, using phred quality scores and the CIGAR string to determine if it is correct. | |
| bool | populateDBSNP (mmapArrayBool_t &dbSNP, IFILE inputFile) const |
| bool | loadDBSNP (mmapArrayBool_t &dbSNP, const char *inputFileName) const |
| user friendly dbSNP loader. | |
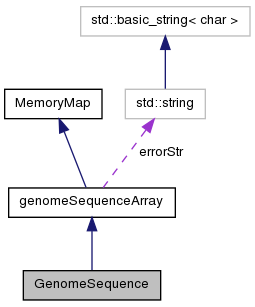
Create/Access/Modify/Load Genome Sequences stored as binary mapped files.
GenomeSequence is designed to be a high performance shared access reference object.
It is implemented as a MemoryMapArray template object with unsigned 8 bit ints, each of which stores two bases. Although 2 bits could be used, most references have more than four symbols (usually at least including 'N', indicating an unknown or masked out base).
Normal use of this class follows these steps:
Sharing is accomplished using the mmap() function via the MemoryMap base class. This allows a potentially large genome reference to be shared among a number of simultaneously executing instances of one or more programs sharing the same reference.
Definition at line 99 of file GenomeSequence.h.
| GenomeSequence::GenomeSequence | ( | std::string & | referenceFilename | ) | [inline] |
attempt to open an existing sequence
| referenceFilename | the name of the reference fasta file to open |
| debug | if true, additional debug information is printed |
Definition at line 128 of file GenomeSequence.h.
{
constructorClear();
setup(referenceFilename.c_str());
}
| GenomeSequence::GenomeSequence | ( | const char * | referenceFilename | ) | [inline] |
Smarter constructor - attempt to open an existing sequence.
| referenceFilename | the name of the reference fasta file to open |
| debug | if true, additional debug information is printed |
Definition at line 138 of file GenomeSequence.h.
{
constructorClear();
setup(referenceFilename);
}
| bool GenomeSequence::checkRead | ( | std::string & | read, |
| std::string & | qualities, | ||
| std::string & | cigar, | ||
| int & | sumQ, | ||
| int & | gapOpenCount, | ||
| int & | gapExtendCount, | ||
| int & | gapDeleteCount, | ||
| std::string & | result | ||
| ) | const |
check a SAM format read, using phred quality scores and the CIGAR string to determine if it is correct.
| read | the read in base space |
| qualities | the phred encoded qualities (Sanger, not Illumina) |
| cigar | the SAM file CIGAR column |
| sumQ | if >0 on entry, is checked against the computed sumQ |
| insertions | count of insertions found in |
| char GenomeSequence::getBase | ( | const char * | chromosomeName, |
| unsigned int | chromosomeIndex | ||
| ) | const [inline] |
given a chromosome name and 1-based position, return the reference base.
| chromosomeName | name of the chromosome - exact match only |
| chromosomeIndex | 1-based chromosome position |
Definition at line 388 of file GenomeSequence.h.
References getGenomePosition().
Referenced by PileupElement::getRefBase().
{
genomeIndex_t index =
getGenomePosition(chromosomeName, chromosomeIndex);
if(index == INVALID_GENOME_INDEX)
{
// Invalid position, so return 'N'
return('N');
}
return((*this)[index]);
}
| int GenomeSequence::getChromosome | ( | genomeIndex_t | position | ) | const |
given a whole genome index, get the chromosome it is located in
This is done via a binary search of the chromosome table in the header of the mapped file, so it is O(log(N))
| 0-based | position the base in the genome |
Definition at line 737 of file GenomeSequence.cpp.
Referenced by getGenomePosition().
{
if (position == INVALID_GENOME_INDEX) return INVALID_CHROMOSOME_INDEX;
if (header->_chromosomeCount == 0)
return INVALID_CHROMOSOME_INDEX;
int start = 0;
int stop = header->_chromosomeCount - 1;
// eliminate case where position is in the last chromosome, since the loop
// below falls off the end of the list if it in the last one.
if (position > header->_chromosomes[stop].start)
return (stop);
while (start <= stop)
{
int middle = (start + stop) / 2;
if (position >= header->_chromosomes[middle].start && position < header->_chromosomes[middle + 1].start)
return middle;
if (position == header->_chromosomes[middle + 1].start)
return (middle + 1);
if (position > header->_chromosomes[middle + 1].start)
start = middle + 1;
if (position < header->_chromosomes[middle].start)
stop = middle - 1;
}
return -1;
}
| int GenomeSequence::getChromosome | ( | const char * | chromosomeName | ) | const |
given a chromosome name, return the chromosome index
This is done via a linear search of the chromosome table in the header of the mapped file, so it is O(N)
| chromosomeName | the name of the chromosome - exact match only |
Definition at line 814 of file GenomeSequence.cpp.
{
unsigned int i;
for (i=0; i<header->_chromosomeCount; i++)
{
if (strcmp(header->_chromosomes[i].name, chromosomeName)==0)
{
return i;
}
}
return INVALID_CHROMOSOME_INDEX;
}
| int GenomeSequence::getChromosomeCount | ( | ) | const |
Return the number of chromosomes in the genome.
Definition at line 731 of file GenomeSequence.cpp.
{
return header->_chromosomeCount;
}
| genomeIndex_t GenomeSequence::getChromosomeSize | ( | int | chromosomeIndex | ) | const [inline] |
given a chromosome, return its size in bases
| 0-based | chromosome index |
Definition at line 256 of file GenomeSequence.h.
{
if (chromosomeIndex==INVALID_CHROMOSOME_INDEX) return 0;
return header->_chromosomes[chromosomeIndex].size;
}
| genomeIndex_t GenomeSequence::getChromosomeStart | ( | int | chromosomeIndex | ) | const [inline] |
given a chromosome, return the genome base it starts in
| 0-based | chromosome index |
Definition at line 246 of file GenomeSequence.h.
{
if (chromosomeIndex==INVALID_CHROMOSOME_INDEX) return INVALID_GENOME_INDEX;
return header->_chromosomes[chromosomeIndex].start;
}
| uint8_t* GenomeSequence::getDataPtr | ( | genomeIndex_t | index | ) | [inline] |
obtain the pointer to the raw data for other access methods
this is a fairly ugly hack to reach into the raw genome vector, get the byte that encodes two bases, and return it. This is used by karma ReadIndexer::getSumQ to compare genome matchines by byte (two bases at a time) to speed it up.
Definition at line 422 of file GenomeSequence.h.
{
return ((uint8_t *) data + index/2);
}
| genomeIndex_t GenomeSequence::getGenomePosition | ( | const char * | chromosomeName, |
| unsigned int | chromosomeIndex | ||
| ) | const |
given a chromosome name and position, return the genome position
| chromosomeName | name of the chromosome - exact match only |
| chromosomeIndex | 1-based chromosome position |
Definition at line 779 of file GenomeSequence.cpp.
Referenced by SamTags::createMDTag(), getBase(), SamQuerySeqWithRefIter::reset(), SamQuerySeqWithRef::seqWithEquals(), and SamQuerySeqWithRef::seqWithoutEquals().
{
genomeIndex_t i = getGenomePosition(chromosomeName);
if (i == INVALID_GENOME_INDEX) return INVALID_GENOME_INDEX;
return i + chromosomeIndex - 1;
}
| genomeIndex_t GenomeSequence::getGenomePosition | ( | int | chromosome, |
| unsigned int | chromosomeIndex | ||
| ) | const |
given a chromosome index and position, return the genome position
| chromosome | index of the chromosome |
| chromosomeIndex | 1-based chromosome position |
Definition at line 788 of file GenomeSequence.cpp.
{
if (chromosome<0 || chromosome >= (int) header->_chromosomeCount) return INVALID_GENOME_INDEX;
genomeIndex_t i = header->_chromosomes[chromosome].start;
if (i == INVALID_GENOME_INDEX) return INVALID_GENOME_INDEX;
return i + chromosomeIndex - 1;
}
| int GenomeSequence::getMismatchCount | ( | std::string & | read, |
| genomeIndex_t | location, | ||
| char | exclude = '\0' |
||
| ) | const [inline] |
Return the mismatch count, disregarding CIGAR strings.
| read | is the sequence we're counting mismatches in |
| location | is where in the genmoe we start comparing |
| exclude | is a wildcard character (e.g. '.' or 'N') |
Definition at line 488 of file GenomeSequence.h.
{
int mismatchCount = 0;
for (uint32_t i=0; i<read.size(); i++)
if (read[i]!=exclude) mismatchCount += read[i]!=(*this)[location + i];
return mismatchCount;
};
| genomeIndex_t GenomeSequence::getNumberBases | ( | ) | const [inline] |
return the number of bases represented in this reference
Definition at line 216 of file GenomeSequence.h.
Referenced by loadDBSNP(), and operator[]().
{
return getElementCount();
}
| int GenomeSequence::getSumQ | ( | std::string & | read, |
| std::string & | qualities, | ||
| genomeIndex_t | location | ||
| ) | const [inline] |
brute force sumQ - no sanity checking
| read | shotgun sequencer read string |
| qualities | phred quality string of same length |
| location | the alignment location to check sumQ |
Definition at line 501 of file GenomeSequence.h.
{
int sumQ = 0;
for (uint32_t i=0; i<read.size(); i++)
sumQ += (read[i]!=(*this)[location + i] ? (qualities[i]-33) : 0);
return sumQ;
};
| bool GenomeSequence::isColorSpace | ( | ) | const [inline] |
tell us if we are a color space reference or not
Definition at line 209 of file GenomeSequence.h.
Referenced by operator[]().
{
return _colorSpace;
}
| bool GenomeSequence::loadDBSNP | ( | mmapArrayBool_t & | dbSNP, |
| const char * | inputFileName | ||
| ) | const |
user friendly dbSNP loader.
| inputFileName | may be empty, point to a text file or a dbSNP vector file |
In all cases, dbSNP is returned the same length as this genome.
When no SNPs are loaded, all values are false.
When a text file is given, the file is parsed with two space separated columns - the first column is the chromosome name, and the second is the 1-based chromosome position of the SNP.
Definition at line 1301 of file GenomeSequence.cpp.
References MemoryMapArray< elementT, indexT, cookieVal, versionVal, accessorFunc, setterFunc, elementCount2BytesFunc, arrayHeaderClass >::create(), getNumberBases(), ifclose(), ifopen(), and MemoryMapArray< elementT, indexT, cookieVal, versionVal, accessorFunc, setterFunc, elementCount2BytesFunc, arrayHeaderClass >::open().
{
//
// the goal in this section of code is to allow the user
// to either specify a valid binary version of the SNP file,
// or the original text file that it gets created from.
//
// To do this, we basically open, sniff the error message,
// and if it claims it is not a binary version of the file,
// we go ahead and treat it as the text file and use the
// GenomeSequence::populateDBSNP method to load it.
//
// Further checking is really needed to ensure users don't
// mix a dbSNP file for a different reference, since it is really
// easy to do.
//
if (strlen(inputFileName)!=0)
{
std::cerr << "Load dbSNP file '" << inputFileName << "': " << std::flush;
if (dbSNP.open(inputFileName, O_RDONLY))
{
//
// failed to open, possibly due to bad magic.
//
// this is really awful ... need to have a return
// code that is smart enough to avoid this ugliness:
//
if (dbSNP.getErrorString().find("wrong type of file")==std::string::npos)
{
std::cerr << "Error: " << dbSNP.getErrorString() << std::endl;
exit(1);
}
//
// we have a file, assume we can load it as a text file
//
IFILE inputFile = ifopen(inputFileName, "r");
if(inputFile == NULL)
{
std::cerr << "Error: failed to open " << inputFileName << std::endl;
exit(1);
}
std::cerr << "(as text file) ";
// anonymously (RAM resident only) create:
dbSNP.create(getNumberBases());
// now load it into RAM
populateDBSNP(dbSNP, inputFile);
ifclose(inputFile);
}
else
{
std::cerr << "(as binary mapped file) ";
}
std::cerr << "DONE!" << std::endl;
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
| bool GenomeSequence::open | ( | bool | isColorSpace = false, |
| int | flags = O_RDONLY |
||
| ) |
open the reference specified using GenomeSequence::setReferenceName
| isColorSpace | open the color space reference |
| flags | pass through to the ::open() call (O_RDWR lets you modify the contents) |
Definition at line 182 of file GenomeSequence.cpp.
{
bool rc;
if (isColorSpace)
{
_umfaFilename = _baseFilename + "-cs.umfa";
}
else
{
_umfaFilename = _baseFilename + "-bs.umfa";
}
if(access(_umfaFilename.c_str(), R_OK) != 0)
{
// umfa file doesn't exist, so try to create it.
if(create(isColorSpace))
{
// Couldon't access or create the umfa.
std::cerr << "GenomeSequence::open: failed to open file "
<< _umfaFilename
<< " also failed creating it."
<< std::endl;
return true;
}
}
rc = genomeSequenceArray::open(_umfaFilename.c_str(), flags);
if (rc)
{
std::cerr << "GenomeSequence::open: failed to open file "
<< _umfaFilename
<< std::endl;
return true;
}
_colorSpace = header->_colorSpace;
return false;
}
| bool GenomeSequence::open | ( | const char * | filename, |
| int | flags = O_RDONLY |
||
| ) | [inline, virtual] |
open the given file as the genome (no filename munging occurs).
| filename | the name of the file to open |
| flags | pass through to the ::open() call (O_RDWR lets you modify the contents) |
Reimplemented from MemoryMapArray< elementT, indexT, cookieVal, versionVal, accessorFunc, setterFunc, elementCount2BytesFunc, arrayHeaderClass >.
Definition at line 159 of file GenomeSequence.h.
{
_umfaFilename = filename;
// TODO - should this method be doing something???
return false;
}
| char GenomeSequence::operator[] | ( | genomeIndex_t | index | ) | const [inline] |
Return the bases in base space or color space for within range index, ot.
| index | the array-like index (0 based). |
NB: bounds checking here needs to be deprecated - do not assume it will exist - the call must clip reads so that this routine is never called with a index value larger than the genome.
The reason for this is simply that this routine gets called hundreds of billions of time in one run of karma, which will absolutely kill performance. Every single instruction here matters a great, great deal.
Definition at line 361 of file GenomeSequence.h.
References BaseAsciiMap::baseNIndex, getNumberBases(), BaseAsciiMap::int2base, BaseAsciiMap::int2colorSpace, and isColorSpace().
{
uint8_t val;
if (index < getNumberBases())
{
if ((index&1)==0)
{
val = ((uint8_t *) data)[index>>1] & 0xf;
}
else
{
val = (((uint8_t *) data)[index>>1] & 0xf0) >> 4;
}
}
else
{
val = BaseAsciiMap::baseNIndex;
}
val = isColorSpace() ? BaseAsciiMap::int2colorSpace[val] :
BaseAsciiMap::int2base[val];
return val;
}
| void GenomeSequence::setApplication | ( | std::string | application | ) | [inline] |
set the application name in the binary file header
| application | name of the application |
Definition at line 194 of file GenomeSequence.h.
{
_application = application; // used in ::create() to set application name
}
| bool GenomeSequence::setReferenceName | ( | std::string | referenceFilename | ) |
set the reference name that will be used in open()
| referenceFilename | the name of the reference fasta file to open |
Definition at line 254 of file GenomeSequence.cpp.
{
if (HAS_SUFFIX(referenceFilename, ".fa"))
{
_referenceFilename = referenceFilename;
_baseFilename = _referenceFilename.substr(0, referenceFilename.size() - 3);
}
else if (HAS_SUFFIX(referenceFilename, ".umfa"))
{
_baseFilename = referenceFilename.substr(0, referenceFilename.size() - 5);
}
else if (HAS_SUFFIX(referenceFilename, "-cs.umfa"))
{
_baseFilename = referenceFilename.substr(0, referenceFilename.size() - 8);
}
else if (HAS_SUFFIX(referenceFilename, "-bs.umfa"))
{
_baseFilename = referenceFilename.substr(0, referenceFilename.size() - 8);
}
else
{
_baseFilename = referenceFilename;
}
_fastaFilename = _baseFilename + ".fa";
if (HAS_SUFFIX(referenceFilename, ".fasta"))
{
_referenceFilename = referenceFilename;
_baseFilename = _referenceFilename.substr(0, referenceFilename.size() - 6);
_fastaFilename = _baseFilename + ".fasta";
}
return false;
}